FAX
F-CODE COMMUNICATION
This function allows the machine to communicate with other machines that also support F-code.
It enables exchange of confidential documents (confidential communication), retrieval (polling) and distribution (polling memory) of information, distribution of information to multiple destinations (relay broadcast transmission) with other machines that support F-code communication. An F-code* is specified in each communication, enabling a higher level of security.
* F-code is a communication function based on the G3 standard of the ITU-T.
The ITU-T is a United Nations organization that establishes communications standards.
It is a department of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), which coordinates global telecommunications networks and services.
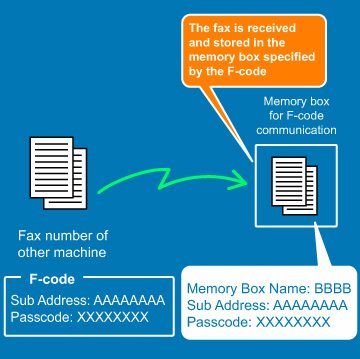
How F-codes work
A fax that is transmitted with an F-code is received in the memory box of F-code communication in the receiving machine specified by the F-code (sub-address and passcode). If the F-code sent by the transmitting machine does not match the F-code in the receiving machine, reception will not take place.
The products of other manufacturers may use different terms for "sub-address" and "passcode". If you need to contact the operator of another machine regarding sub-addresses and passcodes, refer to the terms used by the ITU-T in the table below.
| The machine | ITU-T | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| F-code polling memory box | F-code confidential box | F-code relay broadcasting function | |
| Sub Address | SEP | SUB | SUB |
| Passcode | PWD | SID | SID |
An F-code consists of a sub-address and passcode, and cannot be longer than 20 digits.